Warehouse design is a strategic supply chain management activity that organizes and optimizes storage space for maximum efficiency. Effective warehouse layout planning reduces operating costs by up to 30%, accelerates order processing, improves inventory accuracy, and ensures workplace safety through systematic space allocation and equipment arrangement. join Vinatech Group to explore pricing information!
What is Warehouse Design?
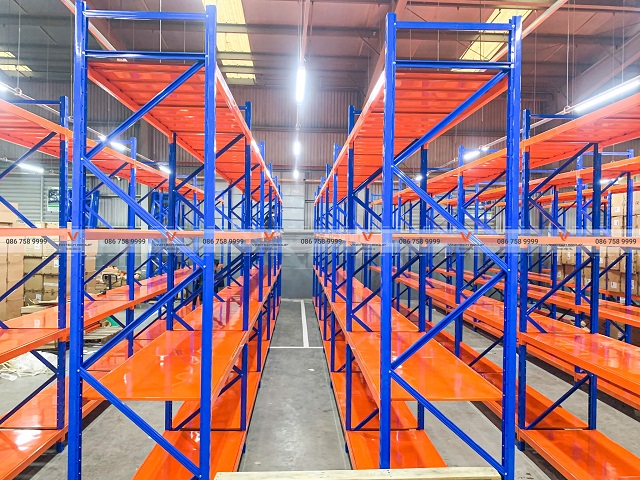
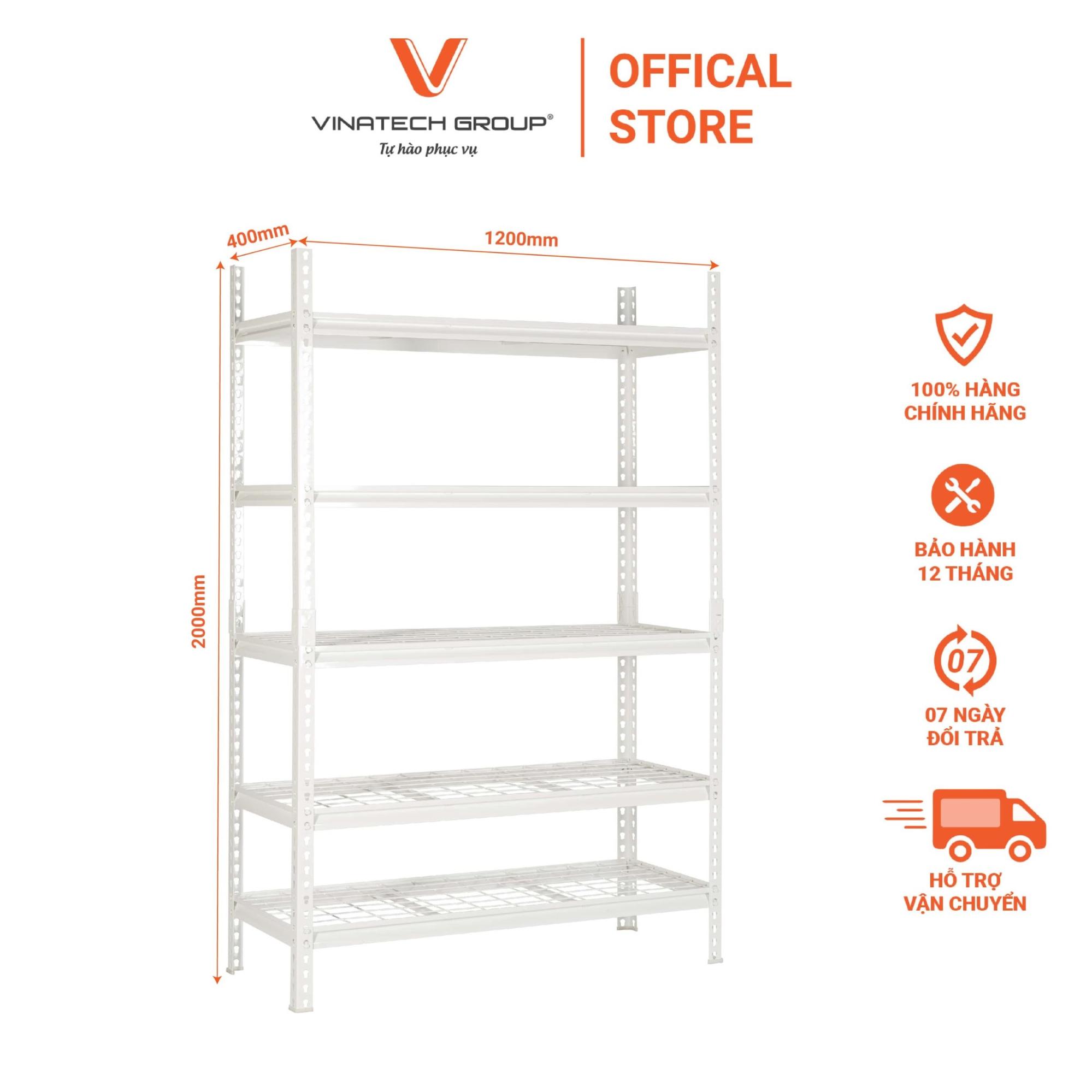
Warehouse design involves detailed planning of functional zones including receiving areas, storage sections, packing zones, and dispatch areas, while arranging racking systems, aisles, material handling equipment, and safety systems appropriate to operational scale.
Effective warehouse design optimizes usable space and accelerates order fulfillment, playing a crucial role in reducing operating costs, enhancing inventory management accuracy, and ensuring worker safety. Design must be executed by experienced teams who understand technical standards and can analyze actual business operational requirements.
Vinatech Group emphasizes that investing in systematic warehouse design from the outset helps businesses increase competitiveness, minimize operational errors, and ensure flexibility when expanding or upgrading systems in the future.
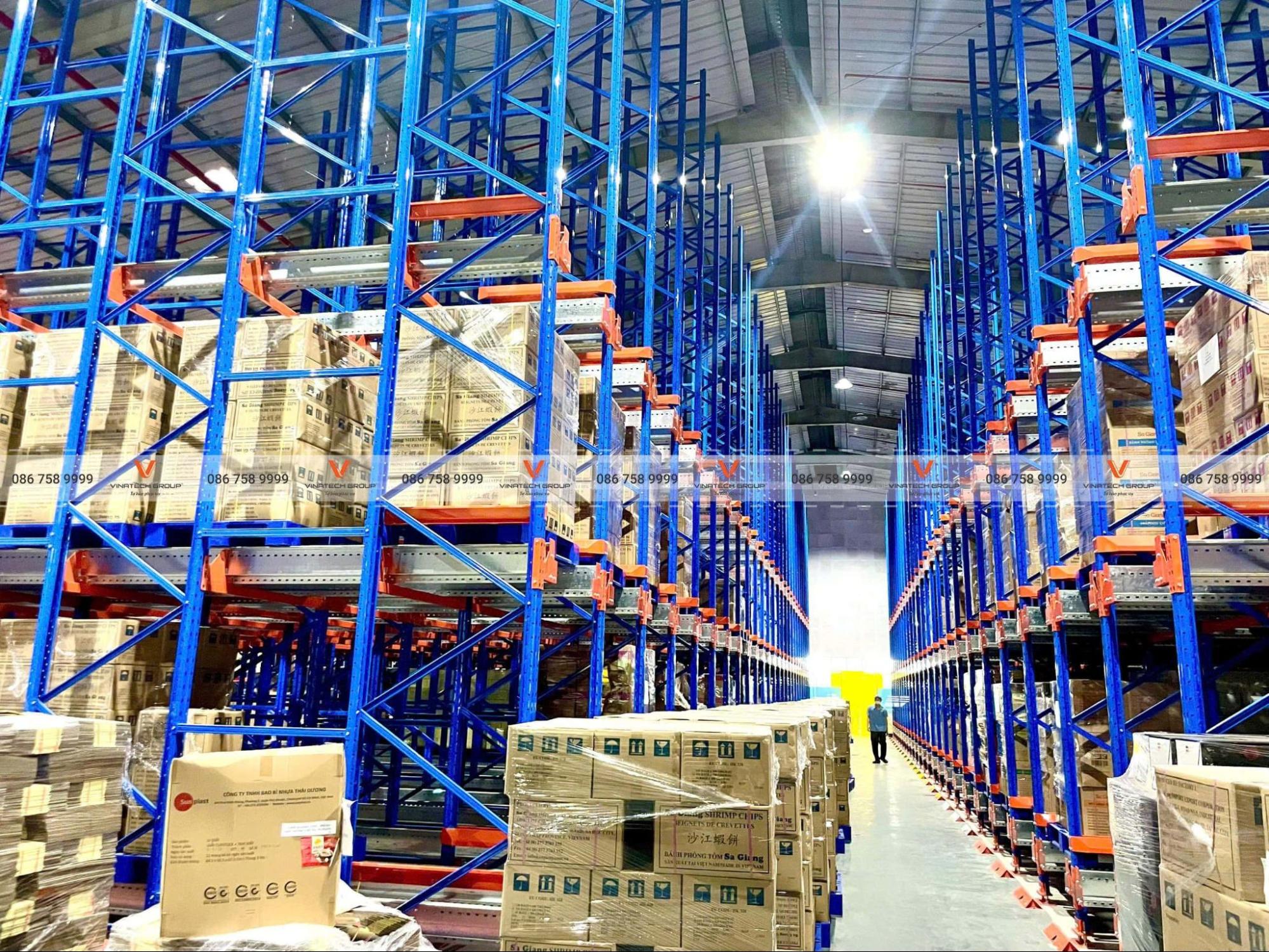

Strategic Importance of Optimized Warehouse Design
- Space optimization: Well-designed warehouses maximize storage capacity, utilize every corner efficiently, and improve goods management.
- Increased productivity: Proper design accelerates inbound/outbound operations, reduces errors, and when combined with standardized workflows, saves time and boosts labor productivity.
- Cost savings: Careful planning reduces initial investment while optimizing workforce requirements within warehouses, decreasing operational expenses.
- Cleanliness maintenance: Smart warehouse designs with organized goods placement facilitate cleaning and maintenance, enhancing aesthetics while protecting inventory from pests and damage.
- Improved overall warehouse management: Organized systems enable smooth operations, rapid goods movement, creating professional environments that enhance productivity and business reputation.
Common Warehouse Design Layouts
U-Shaped Layout
U-shaped warehouse arrangements stand out for simplicity and high efficiency, suitable for most warehouse scales. In this design, the receiving (Loading) and shipping areas are positioned near or adjacent to each other, minimizing internal transportation time.
The receiving process begins by bringing goods to the intake area where items are carefully inspected and sorted before storage, enhancing efficiency and rational storage arrangement.
I-Shaped Layout
I-shaped warehouse layouts are highly rated for reducing aisle quantities and forklift travel distances through straight-line end-to-end operations. The operational sequence begins at the loading/unloading area, proceeds to reception and sorting, then moves goods onto racks in the storage area.
The I-layout perfectly suits FIFO (First In, First Out) management principles. Goods placed near shipping areas receive priority usage, ensuring high-turnover items remain near dispatch zones, minimizing retrieval time and effort.
L-Shaped Layout
L-shaped warehouses create two perpendicular sides forming storage areas. Arranging loading/unloading and shipping areas on adjacent sides significantly reduces warehouse congestion—a popular layout in industrial and logistics sectors.

Essential Warehouse Design Zones
Receiving Area
This zone accepts incoming goods, conducts quality inspections, and potentially sorts products based on characteristics. The receiving area should be adjacent to docks with adequate space to manage all daily incoming goods. If possible, reserve flexible buffer areas for unexpected surges in incoming inventory.
If goods require adjustment upon receipt, additional space and resources are necessary, including personnel, working equipment systems, and areas for new packaging materials and disposal of old packaging systems.
Storage Area
Storage area design depends on whether goods preparation on racking systems is required. In distribution centers, this area may combine one or multiple solutions. For warehouses with diverse products, varying quantities, and different turnover rates, complex storage requirements demand careful planning.
Storage area planning considerations:
First: Research goods turnover rates (rotation ratios), categorizing them into three levels: low, medium, high. Products near average rates are classified as medium turnover. Items significantly lower become low category, while higher items become high category.
Second: Position products based on turnover characteristics:
- Low-turnover goods: Consumed in small quantities, requiring less storage space
- Medium-turnover goods: Selected frequently in moderate quantities, needing balanced rotation speed and easy access
- High-turnover goods: Requested frequently with high demand, requiring maximum rotation capability
Storage configurations typically include:
- Block storage or compact storage areas: Used for high-turnover products where volume matters more than rotation capability
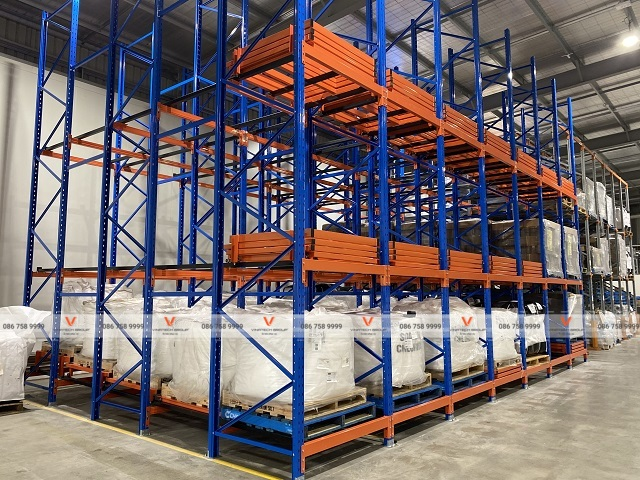
- Selective racking areas: Based on high-turnover product quantities, selective racking systems combined with lower pallet levels facilitate picking
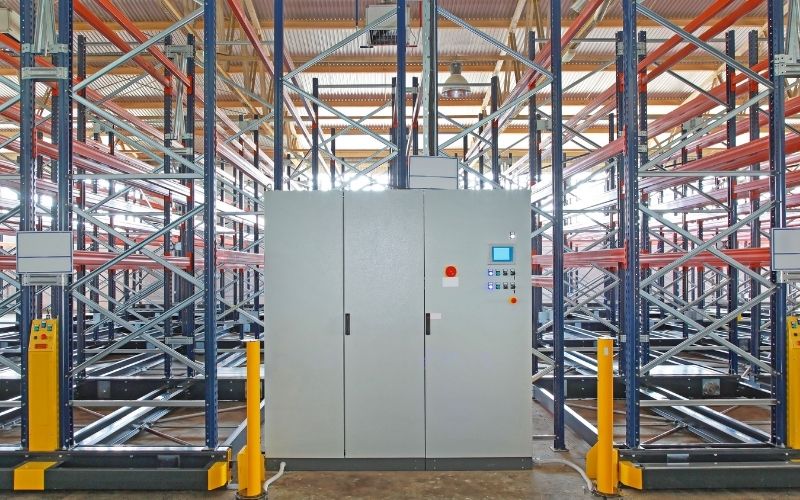
- Equipment selection options: Standard forklifts (3.5m-4.0m aisles), reach trucks (2.5m-3.2m aisles), VNA forklifts (1.7m-2.2m aisles), or warehouse cranes (under 1.7m aisles)
Equipment selection depends not only on aisle widths but fundamentally on the relationship between required and available storage volume. Consider maximum lifting heights for each equipment type and economic efficiency—more advanced handling equipment costs more, requiring ROI calculations.
Dispatch Area
This area contains both order preparation departments (with orders prepared on floors or from racking units) and coordination departments. This zone prepares and packages orders received from other warehouse locations. If preliminary order preparation occurs on racks, this significantly simplifies work.
Order preparation staff must report to the coordination department, which adjusts their operations to meet external demands. Operationally, if warehouses have management systems programmed correctly, order preparation tasks are limited to placing batched products in designated areas.
This space must accommodate all items shipped during normal working days, with buffer areas for unexpected peak demand surges. The dispatch area should be positioned as close as possible to docks.

Warehouse Area Calculation Formula
Warehouse storage area is calculated using the formula: S = α × F
Where:
- S: Total warehouse area
- α: Floor utilization coefficient
- F: Goods storage area
Floor utilization coefficients by warehouse type:
- General warehouses (α): 1.5 – 1.7
- Enclosed warehouses (α): 1.4 – 1.6
- Outdoor warehouses (α): 1.1 – 1.2
Warehouse Design Principles
Loading/Unloading Zone (Loading & Unloading): Typically constructed outside warehouses where trucks easily access, combining with forklift operations to move goods inside to receiving areas.
Reception Zone: Receives goods from loading areas, performs quality control, and sorts inventory.
Storage Zone: Warehouses require racking systems for goods storage and classification enabling easy inbound/outbound operations. Appropriate racking selection will be analyzed below.
Picking Zone: While not all warehouses have separate packing areas, facilities with continuous inbound/outbound frequencies (like logistics) need dedicated zones for retrieving goods from racks before loading onto trucks. Automated ASRS warehouses using roller conveyors or picking robots save 5× normal processing time.
Shipping Zone: If no separate picking area exists, these tasks occur here. Similarly, if items don’t require packing, adequate space should be reserved for placing items before vehicle loading.


Vinatech Group — Leading manufacturer and provider of warehouse racking and smart storage solutions in Vietnam
📞 Hotline: 086.758.9999
📧 Email: info@vinatechgroup.vn
🌐 Website: vinatechgroup.vn
Office locations:
- Hanoi: 15th Floor, TTC Building, 19 Duy Tan Street, Dich Vong, Cau Giay District
- Da Nang: 219-223 Pham Hung Street, Hoa Xuan, Cam Le District
- Ho Chi Minh City: Lot C2-7, N7 Road, Tan Phu Trung Industrial Park, Cu Chi District