Smart warehouses integrate automated storage systems, robotic retrieval mechanisms, and warehouse management software (WMS) to optimize operations—achieving up to 80% space utilization and 50% labor cost reduction. These facilities use AGVs, conveyor systems, and IoT sensors to automate receiving, storage, picking, and shipping processes with minimal human intervention. join Vinatech Group to explore pricing information!
What Is a Smart Warehouse?
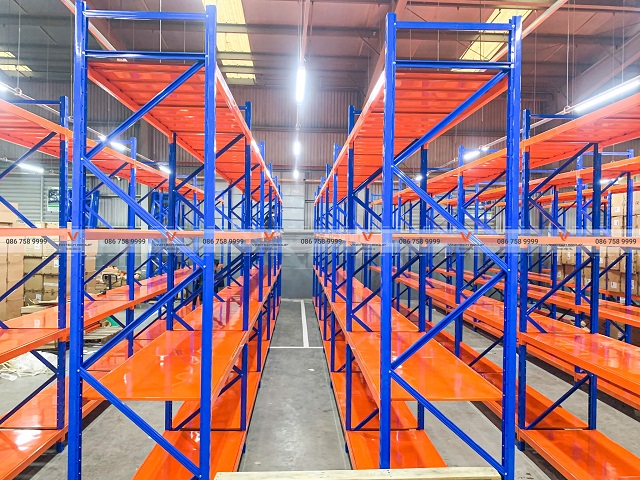
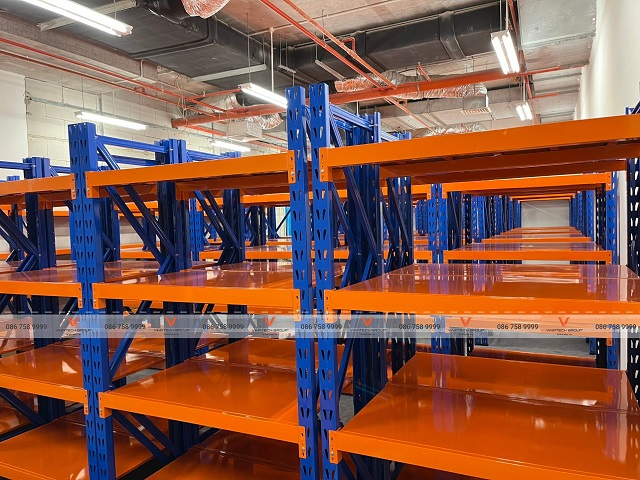
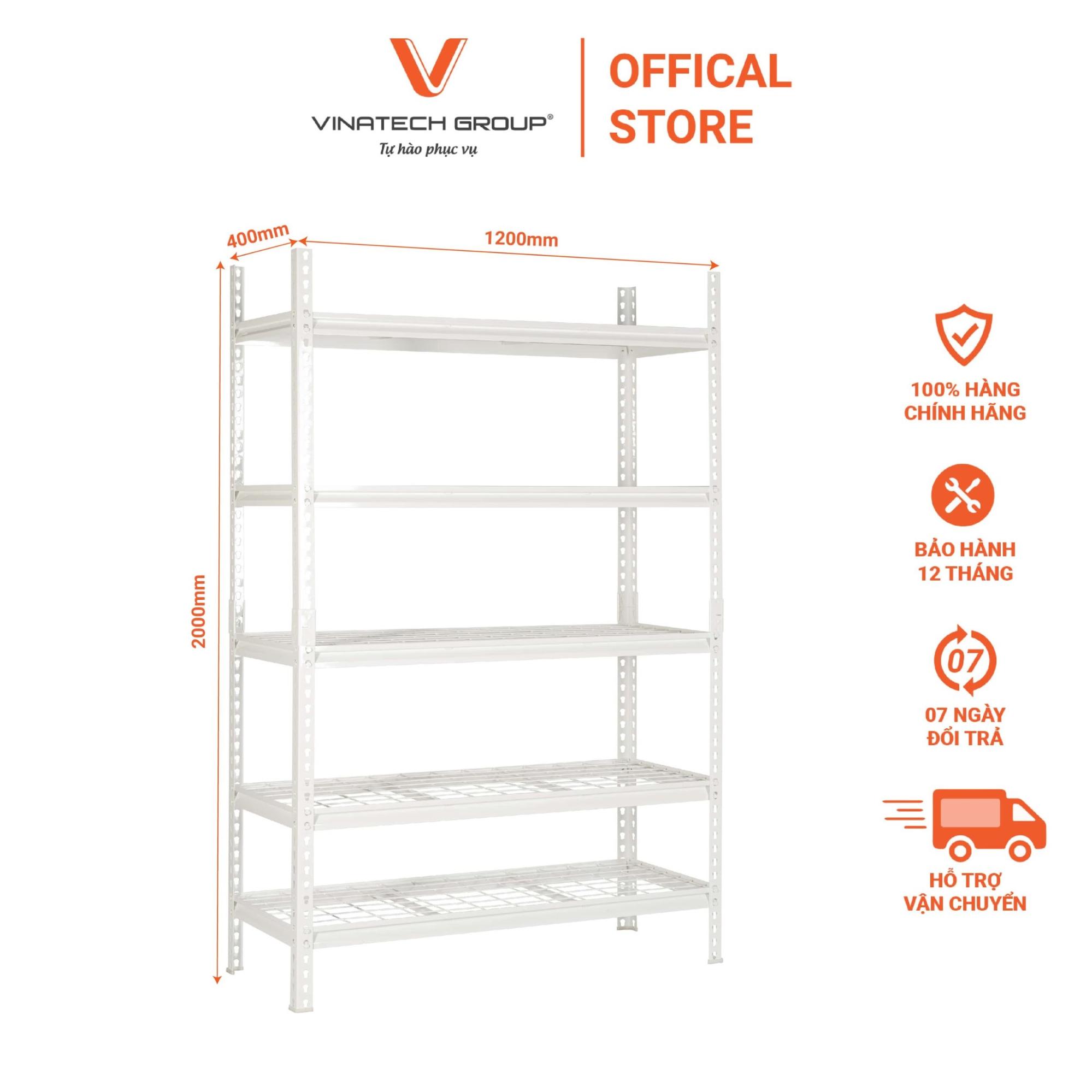
A smart warehouse (also called automated warehouse or intelligent storage facility) is an advanced logistics system that utilizes multi-level racking structures capable of storing goods across multiple tiers while incorporating automated retrieval mechanisms.
These facilities combine automated picking robots, forklifts, cranes, and conveyor systems to transport goods to designated locations. Smart warehouses process orders significantly faster than traditional facilities by replacing manual operations with automated systems.
The solution addresses inefficiencies in conventional warehouse management by implementing automated order reception and confirmation systems. Pick lists are transmitted directly to robotic vehicles that place products into containers and deliver them to workers for subsequent processing.

Key automated operations include:
- Receiving and dispatch: Robots and automated conveyors move goods to storage locations or shipping zones, using barcode scanning, QR codes, and RFID technology for rapid, accurate transactions
- Arrangement and storage: Systems optimize storage positions based on size, weight, and access frequency
- Order picking: Automated systems identify product locations and direct robots to retrieve items on-demand
- Inventory control: Real-time tracking of quantities, locations, and product conditions
- Data analytics: Systems collect and analyze warehouse operations data to optimize performance decisions
What Drives Smart Warehouse Adoption?
Evolving customer expectations demand faster order fulfillment, specialized handling, and enhanced service levels—requiring warehouses that operate with greater agility, faster response times, and optimized labor-equipment productivity.
Technological convergence of robotics, autonomous vehicles, sensor technology, IoT, and advanced racking systems has created the foundation necessary for smart warehouse implementation.

Advantages of Smart Warehouse Implementation
80% Space Optimization, 50% Labor Reduction
Integrated smart solutions improve warehouse efficiency and streamline workflows across diverse operations. Advanced analytics driven by algorithms help warehouse operators manage inventory flow, optimize storage, and eliminate process bottlenecks.
Data-driven approaches not only capture key metrics but enable rational operations that deliver superior customer service. These advanced technologies detect potential supply chain issues and risks early, allowing warehouse managers to be proactive rather than reactive.
- Vertical space utilization: Smart warehouse designs optimize space up to 80% by exploiting vertical storage capacity while maintaining high safety standards. Smart facilities store significantly more pallets than traditional warehouses.
- 50% labor liberation: Fully automated smart warehouse systems require minimal management and handling personnel, substantially reducing labor requirements.

Automated, Rapid, and Accurate Operations
Smart warehouses accelerate order processing times. In non-automated facilities, employees spend most of their day moving around searching for different products—time-consuming and error-prone.
Smart picking equipment like pick-to-light systems, smart glasses, and robotic pickers significantly reduce the time required to locate, verify, and select items from storage bins.
Automated design advantages:
- Each pallet occupies a discrete cell with a unique IP address
- Systems identify precise locations through encoded information (quantity, product code, manufacturing date)
- Warehouse operations become substantially easier
- Inbound/outbound operations proceed automatically and accurately through production lines
Similarly, adding package sorting systems and conveyor systems to transportation processes eliminates lost packages and mislabeling. Faster picking and error-free shipping shortens order fulfillment cycles, providing competitive advantages.
Enhanced Warehouse Management
Typical warehouse operations involve numerous processes and steps vulnerable to errors. These mistakes can cause significant losses across the entire enterprise if not identified and addressed promptly.
One primary advantage of smart warehouse racking systems is higher accuracy at every fulfillment cycle stage. It also reduces lost, damaged, or expired items due to improper inventory management.
Management benefits:
- Smart warehouse designs incorporate robust structural engineering, convenient installation, and simplified maintenance to ensure smooth system operation
- All parameters—product quantities, locations, inventory status—display and update in real-time
- This ensures efficient warehouse management and rapid response to arising situations
Reduced Operating Costs
One major benefit of smart warehouse models is that not every task requires continuous human intervention. Integrating robots, drones, and autonomous vehicles enables partial or complete automation.
Cost savings include:
- Energy conservation through efficiently programmed, optimized, and precise robots
- Reduced workforce, specialized forklifts, and management apparatus within warehouses
- Fast, accurate inbound/outbound operations saving maximum time while delivering high work efficiency
- Effective monitoring and tracking of goods transportation processes
Improved Customer Service
Every warehouse product ultimately reaches consumers. Naturally, customer service, experience, and satisfaction must be prioritized.
With smart warehouse storage capabilities, companies can improve customer interactions, meet changing demands, provide support, and enhance overall experiences. Through faster shipping, reduced costs, and prompt responses, businesses build satisfied customer bases, leading to better customer experiences and satisfaction.
Superior Asset and Inventory Tracking
Effective inventory tracking is one of the greatest concerns for most warehouses. Knowing a specific product’s location in the supply chain helps understand processed orders, improve supply chain planning, and estimate when the next product batch may be needed to prevent stockouts.
In modern warehouses, RFID tags, barcodes, integrated sensors, and other latest technologies provide excellent visibility into product movement and inventory status.
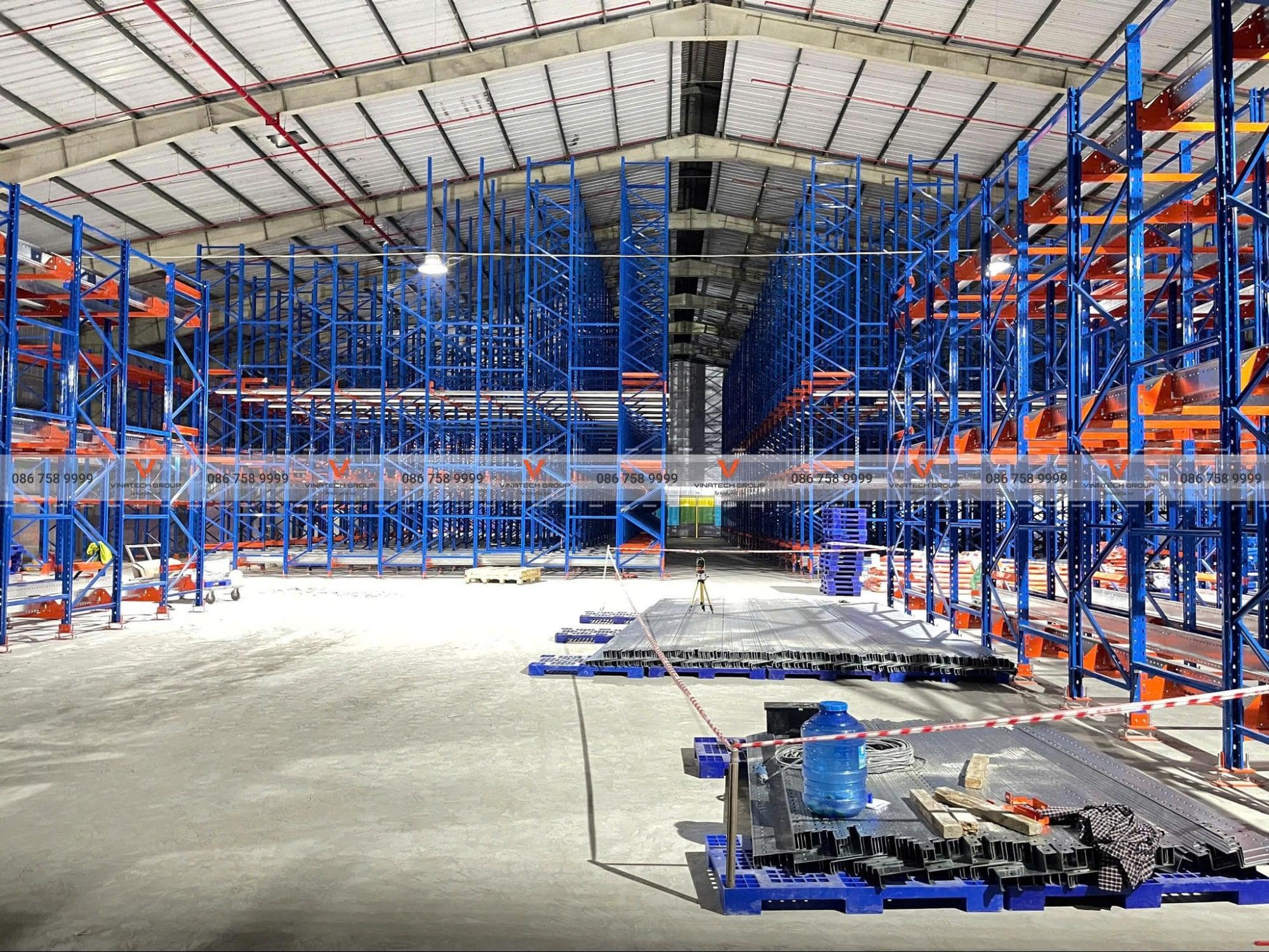

Limitations When Selecting Smart Warehouse Solutions
Initial Capital Investment
Automation technology represents a substantial capital investment. Business owners may hesitate when purchasing new systems. For long-term purchases, automated warehouse systems certainly show profitability. However, short-term ROI remains unclear.
Alongside machinery and technology investment, training employees for proper operation brings time requirements and challenges. The system itself must be programmed to operate efficiently in specific warehouse spaces.
Beyond initial setup and implementation, systems require ongoing maintenance. If systems malfunction, specialists typically must complete repairs. Downtime can be costly. These investments offset some savings achieved through reduced staffing and process optimization.
Limited Adaptability
Automated warehouses implement automation to replace simple, repeatable, time-consuming tasks. In warehouses, changes to inventory or warehouse layout require system reprogramming. In warehouses with consistent products and layouts, adaptability is not a concern.
Workforce Considerations
The primary workforce consideration involves unemployment. With warehouses using automated machinery, available jobs for humans in the warehousing industry will certainly decrease.
Equipment Integrated in Smart Warehouse Systems
Warehouse Management System (WMS)
The warehouse management system serves as the heart of smart warehouses, issuing commands and coordinating all smart warehouse operations.
Warehouse management systems should comprehensively consolidate all critical warehouse data into one easily accessible platform, providing selected supply chain members complete operational visibility, lightning-fast reporting, real-time statistics, and precise planning capabilities.
WMS benefits:
- Real-time access to quality data increases visibility across entire supply chains
- Accurate demand forecasting
- Reduced labor costs through efficient labor allocation
- Streamlined warehouse processes
- Optimized warehouse layout
- Improved picking accuracy
- Reduced time between picks
- Enhanced warehouse flexibility and responsiveness
- Improved warehouse security and safety
- Improved supplier relationships
- Enhanced customer service levels
- Ability to execute continuous optimization strategies
Material Handling Diverter Systems
Material handling diverter systems are comprehensive direction-changing components ensuring smooth operations. They can be divided into several types: 90-degree diverters, 180-degree diverters, and 30-degree diverters.
Key features:
- Fast, efficient material transfer speed
- Smooth operation allowing sorting of multiple product lines
- Low-friction conveyor surfaces, easy cleaning
- Convenient maintenance and repair when malfunctions occur
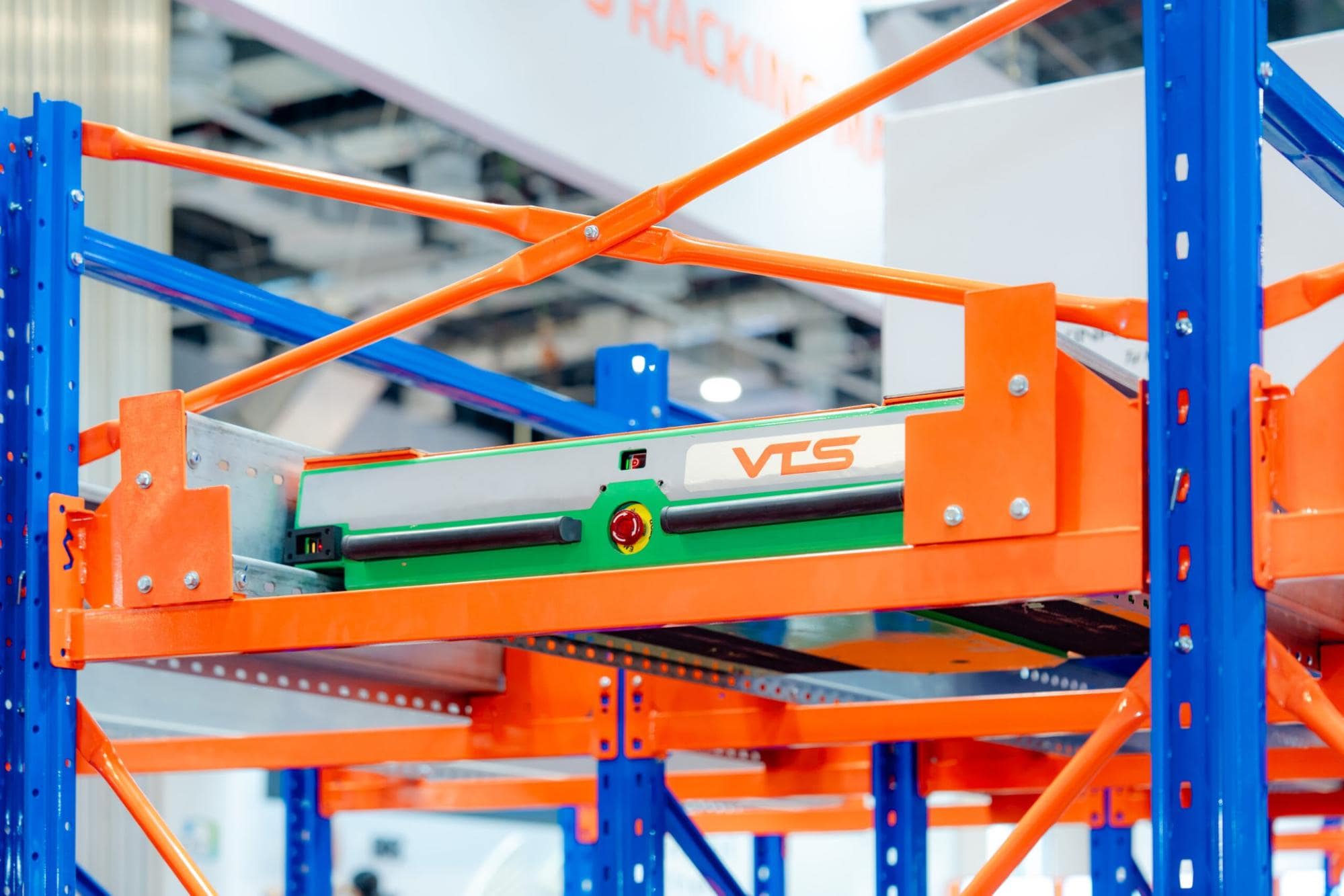
AGV Automated Guided Vehicles
AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) systems represent breakthrough solutions, bringing outstanding improvements to warehouse storage and retrieval operations. These systems completely automate goods transportation—from loading to warehousing—optimizing efficiency and saving business costs.
This is a safe and intelligent solution with AGV autonomous robots suitable for any warehouse.
AGV advantages:
- Moves automatically along pre-installed digital routes, completely eliminating human participation in goods transportation
- Optimizes space and working time
- Increases warehouse storage space by 50-70%
- Increases goods receiving efficiency 2-3 times compared to traditional warehouses
- Operates continuously 24/7 without rest, multiplying goods transportation productivity compared to manual methods
- Equipped with advanced positioning and navigation systems, ensuring accurate route movement and collision avoidance
- Can be easily deployed in existing warehouses without requiring layout or system changes
- Enterprises can flexibly add more AGVs when transportation demands increase
- Automation reduces labor costs, maintenance costs, and accident repair costs
Diverse applications:
- Transporting raw materials, finished products, goods in warehouses
- Transporting components and parts in production lines
- Transporting goods in distribution centers and warehouses
Iterails Electric Conveyor Systems
Rated as the fastest goods transportation system currently installed in warehouses. Two types exist: suspended electric conveyors and floor-running electric conveyors.
System benefits:
- Electric conveyor systems transport goods at high speeds
- Iterails is a versatile transportation system suitable for changing designs or upgrades
Automated Cranes
Automated crane systems accommodate warehouse ceiling heights up to 15m or higher. Can be used for both conventional and smart warehouses.
Automated overhead cranes can be used flexibly without requiring warehouse structural modifications. Automated crane systems move on rails with ground support points and perform loading/unloading operations when receiving control system commands.
Goods Lifts
- Transport goods to higher warehouse levels
- Goods lift systems suit small and medium-sized warehouse models
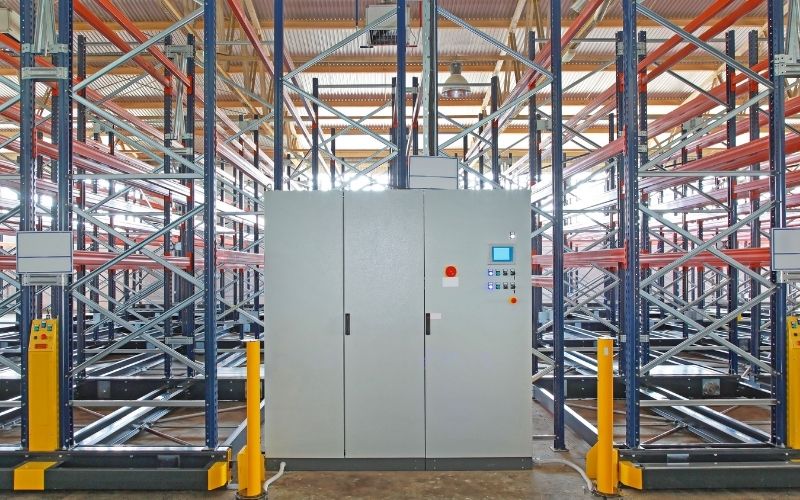
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) have existed for many years, playing crucial roles in improving warehouse efficiency. Previously, AS/RS was often considered expensive, cumbersome, and inflexible.
Today, AS/RS has been significantly improved, overcoming previous limitations and bringing superior benefits to businesses:
AS/RS benefits:
- Completely automates storage and retrieval processes, minimizes labor requirements, saves labor costs, and enhances operational efficiency
- Can be designed modularly, easily expanded or reduced according to business needs, suitable for various warehouse scales
- Operates with high precision, minimizes human errors, ensures goods are stored and retrieved at correct positions, reducing loss and damage
- Thanks to automation and high accuracy, AS/RS accelerates storage and retrieval speeds, optimizes warehouse processes, enhances productivity and operational efficiency
- Provides detailed information management systems about location, quantity, and condition of warehouse goods, helping businesses easily track and control inventory effectively
- Reduces labor accidents from manual goods transportation, creating safer work environments for employees

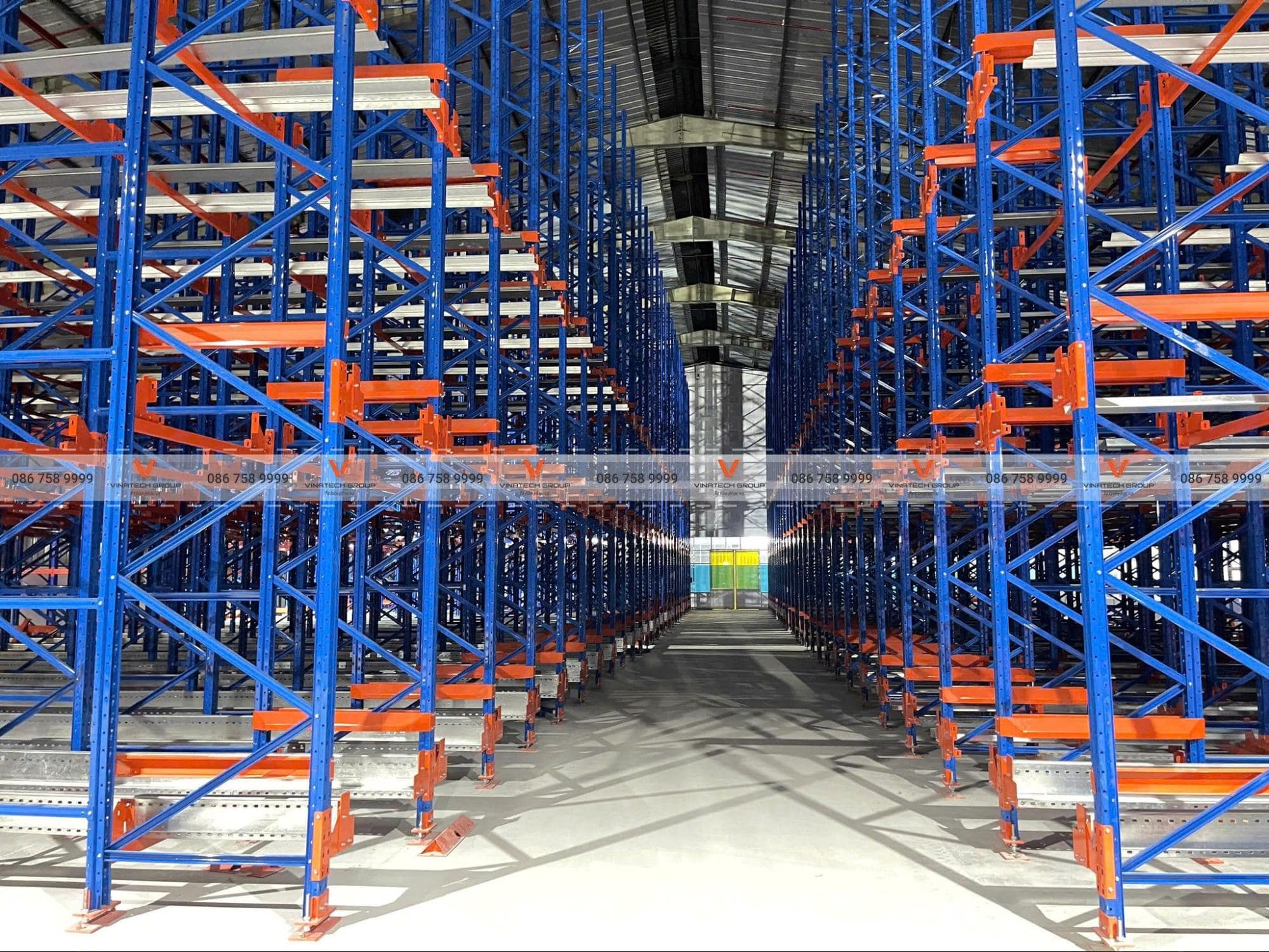
Principles When Applying Smart Warehouse Solutions
Space optimization: Using smart shelving and storage systems optimally utilizes warehouse space most effectively—an indispensable component for building automated storage facilities.
Safety and security: Ensure safety for personnel and equipment through safety measures like collision sensors, surveillance cameras, and access control systems. Protect critical data and systems from threats through security layers.
Rational movement layout: Design goods flow for optimal efficiency to minimize travel time and optimize performance. Ensure conveyors and warehouse aisles are rationally designed to avoid conflicts and congestion.
Warehouse zoning: Divide warehouses into zones for easy location identification and convenient picking and placement operations. Arrange goods based on criteria like usage frequency or product type.
Periodic inspection and maintenance: Conduct regular inspections and maintenance of automated robots and warehouse systems to ensure stable and safe operation. Review repair and maintenance procedures to ensure rapid repair readiness, avoiding supply chain disruptions.
Employee training: Train employees to use and manage smart warehouse equipment and software. Ensure they understand how to perform safety inspections and handle emergency situations.

Smart Warehouse Implementation Costs
Implementing automated warehouse systems (smart warehouses) brings many business benefits, improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing competitive advantages. However, investment costs for these systems concern many businesses.
Smart warehouse implementation costs depend on multiple factors:
- More complex and larger-scale automation systems require higher costs
- Does the business want to automate the entire process or only certain parts? Higher automation levels lead to higher costs
- Businesses with large operational scales storing more goods will have higher costs than small enterprises
Estimated smart warehouse implementation costs:
- Basic solution: 200–300 billion VND
- Advanced solution: 300–500 billion VND
- Comprehensive solution: Over 500 billion VND
Real-World Smart Warehouse Applications
In practice, smart warehouse designs are applied by many large organizations and enterprises to ensure professional, economical, and long-lasting warehouse operations and management.
- Building finished product and raw material warehouses for manufacturing plants, pharmaceuticals, food production
- Building transfer warehouses, distribution warehouses, goods consignment warehouses in the Logistics industry—typically equipped with piece-picking lines to save floor space and minimize workforce
- Building cool warehouses, cold warehouses in frozen food production, vegetable industries
Steps to Establish Smart Warehouse Solutions
Step 1: Evaluate Current Operations
Before transitioning to smart warehouses, businesses must comprehensively examine current operations. Decision-makers must understand workflows, identify inefficiency points, and determine areas that could benefit from automation or smart technology.
This step also involves collecting and analyzing critical warehouse data such as inventory flow, retrieval processes, and labor costs.
Step 2: Define Your Objectives
Once you understand current operations, identify what you want to achieve with your smart warehouse. This could be improving customer service, increasing inventory accuracy, or reducing overall costs.
Clear objectives will guide your technology selection and strategies, ensuring the warehouse aligns with your business goals.
Step 3: Select Appropriate Technology
The next step involves selecting smart technologies to help achieve your objectives. This could be anything from automated guided vehicles for material handling to warehouse management systems for better inventory control or IoT equipment for real-time tracking and data visibility.
When selecting technology, consider its compatibility with existing systems, ease of use, scalability, and potential return on investment.
Step 4: Implementation
After selecting appropriate technology, the next phase involves deploying them in your warehouse. This may include retrofitting your warehouse space to accommodate new equipment, integrating new software with existing systems, or installing IoT devices.
Remember, implementing new technology is a significant change, so careful planning is essential to minimize operational disruption.
Step 5: Training and Support
Deploying new technologies is only half the battle—ensuring your employees can effectively use and manage these systems is equally important. Invest in professional training to help your team understand how to operate new equipment, use new software, and follow updated procedures.
Additionally, ensure you have access to ongoing technical support to address any issues that may arise with your new systems.
Step 6: Review and Optimize
Finally, after your smart warehouse becomes operational, regularly evaluate its performance. Use data collected by smart systems to better understand operations, identify areas for further improvement, and make necessary adjustments.
This continuous review and optimization process is critical to ensuring your warehouse remains efficiently operational long-term.

Smart Warehouse vs. Traditional Warehouse Comparison
| Feature | Smart Warehouse | Traditional Warehouse |
| Operational Process | Most warehouse tasks are automated by smart systems, robots, machinery, and software. Employees only supervise and control systems, minimizing direct participation in manual operations. | Employees move through warehouses with packing slips, manually performing tasks: selecting products, transporting, quality checking, packing, and shipping. |
| Automation Level | High automation level, applying advanced automation solutions like picking robots, automated transport systems (AGV), goods sorting systems | Low automation level, primarily using support equipment like forklifts, elevators operated by humans |
| Operational Efficiency | Enhanced operational efficiency through automation, minimized errors, accelerated order processing speed, and optimized procedures | Operational efficiency depends on human productivity and accuracy, prone to human errors |
| Operating Costs | High initial investment cost but saves labor costs long-term | High labor costs due to large workforce |
| Management Capability | Smart warehouse management systems (WMS) comprehensively track and monitor warehouse operations, provide detailed data and reports, support effective decision-making | Management relies on manual ledgers and reports, difficult to track and monitor warehouse operations |
| Benefits | Enhanced operational efficiency, reduced operating costs, increased inventory control capability, improved customer service, and enhanced competitive capacity | Low investment cost, easy deployment and operation |

Trusted Smart Warehouse Solution Provider
Vinatech Group is proud to be a comprehensive smart warehouse solution provider, helping businesses optimize warehouse management processes, enhance operational efficiency, and increase profitability.
With experienced engineering teams and deep expertise in automation technology and IoT, we commit to delivering optimal solutions appropriate to each business’s specific needs and budgets.
When selecting Vinatech Group’s smart warehouse solutions, you receive:
Smart Warehouse Management System (WMS): Automates warehouse management processes from A to Z, including receiving, dispatching, inventory counting, goods allocation—optimizing operational efficiency and minimizing errors. Provides detailed real-time goods condition information, helping businesses easily track and manage warehouses.
Automated Guided Vehicle Systems (AGV): Automatically moves warehouse goods, minimizes manual labor, enhances productivity and labor safety. Various robot types suit diverse business needs like pulling AGVs, lifting AGVs. Integrates advanced guidance systems like laser, camera, RFID for safe and efficient movement.
Automated Storage/Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): Automatically stores and retrieves goods in high-rise warehouses, optimizes warehouse space, and reduces operating costs. Combines with WMS for effective control and management of forklifts.
Automated Conveyor Systems: Automates goods transportation, enhancing operational efficiency, optimizing costs, and increasing business profitability. Systems include motor-controlled conveyor types that move goods from one location to another automatically without human intervention.
Smart warehouse design represents the future of modern industry—a solution that minimizes human labor, reduces warehouse rental costs, and achieves high work performance.
Vinatech Group — Leading manufacturer and provider of warehouse racking and smart storage solutions in Vietnam
📞 Hotline: 086.758.9999
📧 Email: info@vinatechgroup.vn
🌐 Website: vinatechgroup.vn
Office locations:
- Hanoi: 15th Floor, TTC Building, 19 Duy Tan Street, Dich Vong, Cau Giay District
- Da Nang: 219-223 Pham Hung Street, Hoa Xuan, Cam Le District
- Ho Chi Minh City: Lot C2-7, N7 Road, Tan Phu Trung Industrial Park, Cu Chi District